Recently, new progress has been achieved by Prof. HAN Keli of DICP in the study of the mechanism of nicotine hydroxylation catalyzed by Cytochrome P450 A26 (designated as CYP2A6), when collaborating with Prof. Changguo Zhan of the University of Kentucky, USA, and their research results were published in the newly appearing Journal of American Chemical Society with the title of “Catalytic Mechanism of Cytochrome P450 for 5 -Hydroxylation of Nicotine: Fundamental Reaction Pathways and Stereoselectivity”(J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7416-7427).
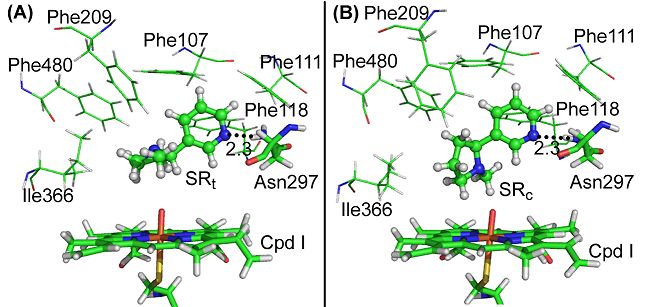
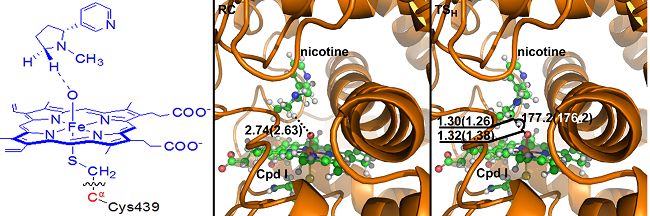
By utilizing methods of molecular docking, molecular kinetic simulation as well as QM/MM computations, the DICP and Kentucky researchers have investigated the combination mode of nicotine and CYP26A, and the mechanism as well as the stereoselectivity of 5-hydroxylation of nicotine catalyzed by CYP2A6. Their results showed that, although nicotine exists mainly as a protonated species in solution, it is combining with the active sites of CYP2A6 in non-protonated forms of SRt and SRc. In the CYP2A6-nicotine complex, the N atom of the pyridine ring forms a hydrogen-bond with the Asn297 site of the CYP2A6, and there is a π-π interaction between the pyridine ring and the surrounding phenylalanine, such that the trans-5-H or the cis-5-H in the pyrrolidine ring is pointing to the O atom of the Cpd I site of the CYP2A6. In this way, the occurring of the 5-hydroxylation reaction is favored.