Hydrogen storage is an important topic in the investigation of hydrogen energy applications. At present, the techniques of hydrogen storage mainly involve two categories: chemical storage and physical storage. Physical storage can be realized via physical adsorption by utilizing micro-porous materials. How to enhance the hydrogen adsorption capacity of the micro-porous materials is a key topic in hydrogen storage research.
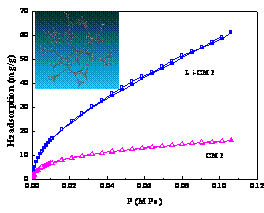
Recently, DICP researcher DENG Weiqiao and his co-workers have succeeded in developing a new kind of adsorption material of three dimensional conjugated polymer(CMP) by catalytic polymerization of acetylenylbenzene. Moreover, when lithium ions were incorporated into this new micro-porous material, its hydrogen adsorption ability could be greatly enhanced. It was shown that under a temperature of 77K and a pressure of 1 bar, the hydrogen storage capacity of this new material was as high as 6.1 wt%, which was a new record for physical hydrogen storage materials, and was much higher than counterpart materials such as carbon nano-materials (3.0 wt%) and metallic frame compounds(2.5 wt%).
These results have been published recently in the journal of Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 3330-3333. DOI:10.1002/anie.200906936).