A paper with the title of “Site-specific photocatalytic splitting of methanol on TiO2(110)” has been published recently in the journal of Chemical Science (2010, 575-580,DOI: 10.1039/C0SC00316F), and was cited as “a highlighted paper”. (http://www.sciencemag.org/content/vol330/issue6000/twil.dtl)
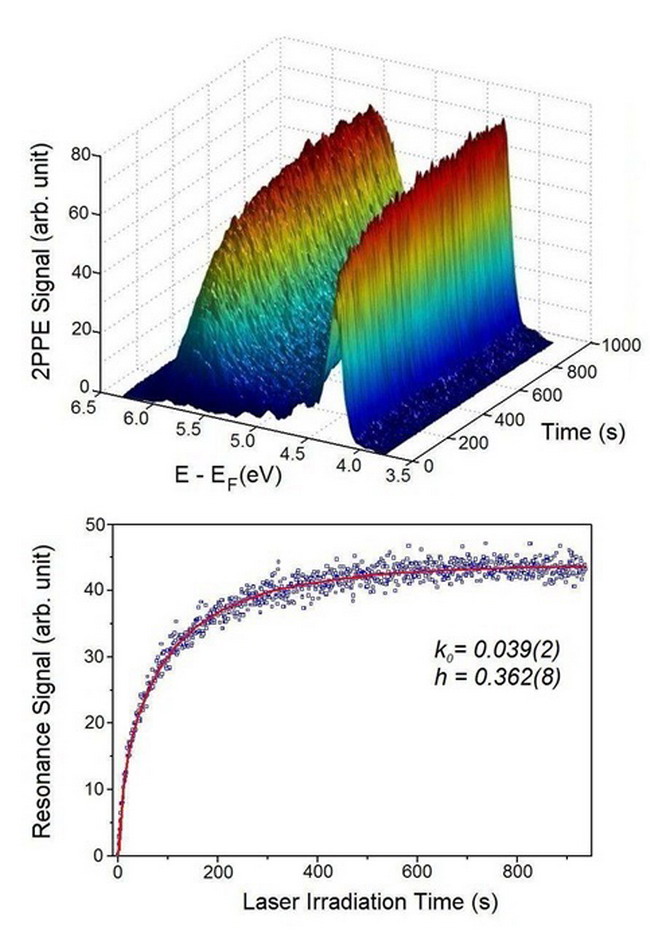
This work was done by the DICP research group headed by Prof. YANG Xueming. It is known that methanol can enhance the efficiency of photocatalytic decomposition of water by TiO2. However, the interaction between methanol and 2 is not clear. If this process can be made clear on a molecular level, it would provide hints for developing more effective photocatalysts. By employing a method of real-time double-photon photoelectron spectrometer (TD-2PPE) developed by themselves, they studied the changes given rise in the double-photon photoelectron spectra during the course of irradiation by UV lights on the TiO2(100) plane covered by monolayer methanol. By combining this method with high-resolution scanning tunnel microscopy experiments, they succeeded in the identifying of direct evidence for photo-splitting of methanol adsorbed on 5 coordinated Ti atoms (5c Ti4+), thus settling the extended controversy over this problem. They have found that the splitting process went through the breaking of the O-H bond, and that the H atom was transferred to the neighboring bridged O atom. DFT(density functional theory) calculation results showed that strong interaction occurred between the newly formed methoxy group and its adsorbing Ti atom. Consequently, the position of the Ti atom was raised, its density of state(DOS) changed, and new electron states appeared at ca. 2.5 eV above the Fermi level. This is consistent with the experimental observation of excited levels 2.4 eV above the Fermi level. Judging from the evolution of the variation of the double-photon photoelectron spectra with time, it is evident that the photo-induced splitting process is a typically heterogeneous process.
These results also showed that the O-H bond in the methanol molecule, when adsorbed on TiO2, possesses photo-chemical activity, and this can explain why adding of methanol to water can enhance the photo-catalytic yield of hydrogen on TiO2. Furthermore, the results indicated that 5 coordinated Ti atoms are also photo-catalytically active, but this significance has not been recognized so far.