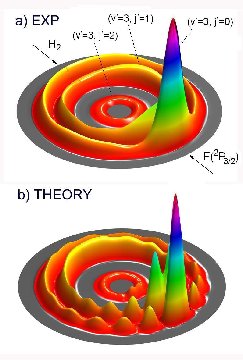
A basic research paper entitled HF(v=3) forward scattering in the F+H2 reaction: Shape resonance and slow-down mechanism has appeared in the recently published journal PNAS (Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences) of USA [Vol. 105,6227-6231(2008)]. The paper was written by Prof. YANG Xueming, Prof. ZHANG Donghui and coworkers.
The mechanism for the formation of the forward scattering of the HF(v=3) product in the F + H2 reaction has puzzled the chemical dynamics researchers for more than 20 years. The phenomenon of the above mentioned forward scattering of the HF(v=3) product was first observed by Y.T. Lee and co-workers in the 1980s. They have speculated that this is due to the resonance states of reaction. However, research outcomes of the 1990s did not give support to their speculation. Recently, the research team headed by Prof. YANG Xueming of DICP has succeeded in determining full quantum state resolved spectra of the F+H2 -> HF(v=3)+H reaction by means of a custom-made cross molecular beam-H atom Rydberg tagging time-of-flight installation. On the other hand, theoretical analysis basing on the potential surface for this reaction, constructed by Prof. ZHANG Donghui of DICP and Prof. XU Xin of Xiamen University, showed that the forward scattering of the HF(v=3) product is resulted from a time lagging effect due to the slowing down of the product when it is passing over the centrifuge potential of the HF(v=3) adiabatic vibration potential. Thus, the combination of highly sophisticated experiments with a precise theoretical analysis has given a clear answer to the long standing puzzle in chemical dynamic studies.